
These are made up of between 3 to 5 vertebrae (usually counted as 4 bones) that are fused together and collectively known as the coccyx or tail bone. The natural curvature is ‘outwards’ (kyphosis) and is known as the central bones of the buttock. S1 to S5) are fused into a single bone known as the sacrum. The normal curvature is ‘inwards’ (lordosis) and is known as the lower back or abdominal back bones. These are the ‘fattest’ of the vertebrae due to the big body of each bone and this section is made up of 5 vertebrae (abbr. The normal curvature is ‘outwards’ (kyphosis). They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and with the axis forms the joint connecting the skull and spine.

T1 to T12) and are the chest back bones of the spinal column. 3d illustration of Skull With Spinal Cord Anatomy. This section is made up of 12 vertebrae (abbr. The normal curvature of the cervical vertebrae is ‘inwards’ (lordosis). The spinal cord finishes growing at the age of 4, while the vertebral column finishes growing at age 14-18. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. It is situated inside the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. C1 to C7) and are the neck bones of the spinal column. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS). This section is made up of 7 vertebrae (abbr. The spinal cord is the neurological pathway for sending and receiving signals to and from the brain. Apart from the structural support function of the spinal column, it also houses and protects the spinal cord, which sends out branches (spinal nerves) to different areas of the body.
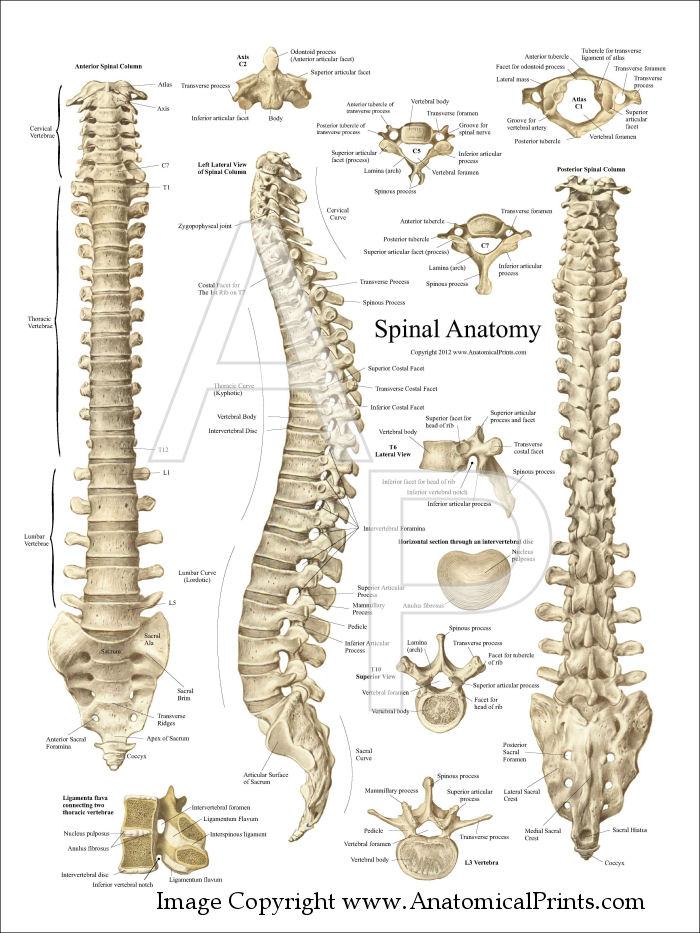

This shape is maintained by four main curvatures of the spine, known as lordosis (convex anterior) when it curves ‘into’ the body or kyphosis (concave anterior) when it curves ‘out’ of the body. The orientation of these bones is maintained by muscles and ligaments to give the normal vertebral column a typical S-shape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
